
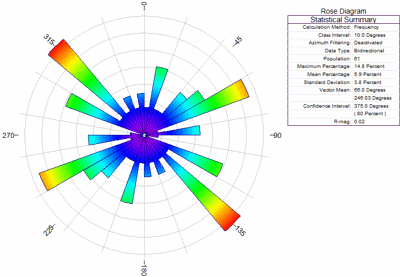
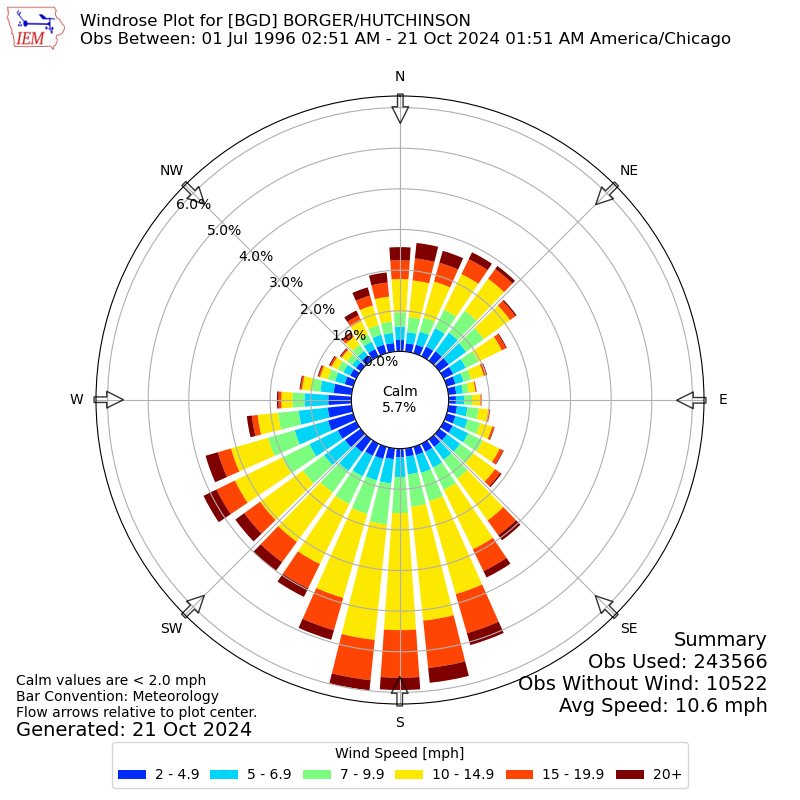
In the last few decades, the use of imagery from satellites, aircraft and UAVs (e.g., Vasuki et al., 2014), and the mapping of seismic reflection data (e.g., Chopra et al., 2009), has led to the generation of much lineament data. Rose diagrams are also widely used to analyse elongate and aligned surface features produced by geomorphological, tectonic and other process, usually referred to as lineaments (e.g., Hobbs, 1904). They generally show the frequency of two-dimensional orientation data, such as winds and waves (since the early 1800s Lalanne, 1843), palaeocurrent directions (since mid-1800s Potter and Pettijohn, 1963), fault and fracture trends (since 1840s Howarth, 1999). Rose diagrams are widely used to depict physical phenomena with directional properties. The aim of the rose diagram is to display the distribution of data in a form that can be easily understood and evaluated. It is possible to weight this by other values, such as length, wind speed, wave height, cost, etc. Where the radial value is some frequency, the rose diagram acts as a form of histogram, with the bars wrapped round a circle (Fig. The variables may be continuous, but are often grouped or binned on the basis of direction. The rose diagram is thus a plot in polar coordinates.

Rose diagrams are widely used plots that represent the relationships between two variables, where one is a direction or angle represented by an angle round a circle in a similar way to a compass rose and the other a scalar quantity represented by the radial distance from the centre of the circle.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
